1,¿Qué es la goma gellan de alta acidez?
Goma Gellan con alto contenido en aciloun extraordinario hidrocoloide, se ha hecho un hueco en la industria alimentaria por sus singulares características gelificantes. Descubierto en los años setenta a partir de la bacteria Sphingomonas elodea, se ha convertido en un ingrediente clave en la elaboración moderna de alimentos. Este biopolímero se produce mediante fermentación microbiana, un proceso que aprovecha los fenómenos naturales para la producción comercial.
Su característica definitoria es el alto contenido en grupos acilo, que le confiere propiedades distintivas en comparación con su homólogo de bajo contenido en acilo. Estos grupos acilo, concretamente el acetato y el glicerato, son los responsables de la textura suave y elástica de la goma, que la distingue de otros gelificantes que suelen producir geles firmes y quebradizos.
La versatilidad de la goma gellan de alto contenido en acilo reside en su capacidad para crear texturas variadas -desde blandas y elásticas hasta firmes y quebradizas- con sólo ajustar su concentración y los iones presentes en la solución. Esta adaptabilidad la convierte en una valiosa herramienta en el arsenal de los tecnólogos alimentarios.
Sus aplicaciones abarcan una amplia gama de productos, desde mejorar la sensación en boca de los productos lácteos hasta proporcionar geles estables en confitería. La diversidad de su uso subraya su importancia en el ámbito de la ciencia y la tecnología alimentarias.
2,Composición química y producción de goma gellan de alto contenido en acilo
Estructura química
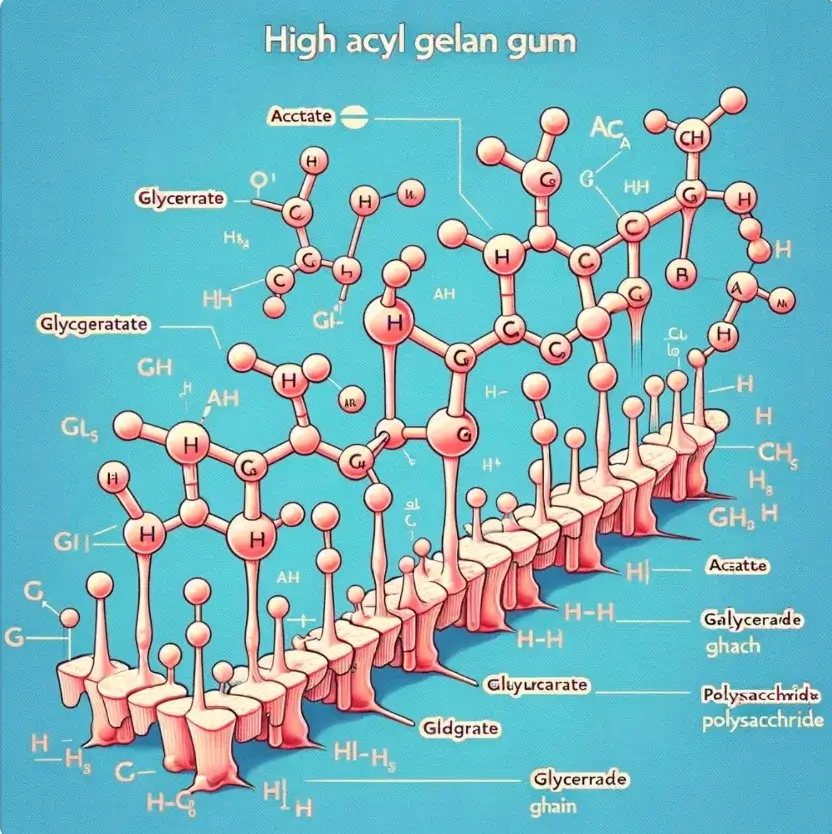
La funcionalidad única de la goma gellan de alto acilo se deriva de su compleja estructura química. En esencia, es un polisacárido formado por una unidad repetitiva de cuatro residuos de azúcar: glucosa, ácido glucurónico, ramnosa y, de nuevo, glucosa. La característica que define a la goma Gellan de alto contenido en acilo es la presencia de sustituyentes acilo: grupos acetato y glicerato. Los grupos acetato están unidos a la posición C-6 de la primera unidad de glucosa, mientras que los grupos glicerato están unidos a la posición C-2 de la tercera unidad de glucosa en la secuencia repetitiva. Estos grupos acilo son fundamentales para conferir a la goma su característica textura suave y elástica.
Proceso de producción
La producción de goma gellan de alto contenido en acilo es una fascinante mezcla de biología y tecnología. Comienza con el cultivo de la bacteria Sphingomonas elodea en un proceso de fermentación controlado. La bacteria sintetiza la goma gellan como polisacárido extracelular. El producto resultante se somete a una serie de etapas de purificación, como precipitación, filtración y secado. Durante estos pasos, la goma se desacilla parcialmente, lo que significa que se eliminan algunos grupos acilo. El grado de desacilación puede controlarse para producir distintos grados de goma gellan: alta y baja en acilo, cada una con propiedades distintas.
Control de calidad y seguridad
El proceso de producción incluye estrictas medidas de control de calidad. Entre ellas se incluyen la supervisión de la pureza microbiana, la garantía de ausencia de contaminantes nocivos y la verificación de la consistencia de las propiedades químicas y físicas del producto. La Goma Gellan de alto contenido en acilo está generalmente reconocida como segura (GRAS) por las autoridades de seguridad alimentaria, y su producción se adhiere a rigurosas normas de seguridad alimentaria.
3,Propiedades y beneficios de la goma gellan de alto contenido en acilo
La goma gellan de alto contenido en acilo posee una serie de propiedades que la convierten en un activo valioso en la tecnología alimentaria y en otras industrias. Estas características no sólo contribuyen a su uso generalizado, sino que también la diferencian de otros hidrocoloides.
Propiedades clave
- Capacidad de gelificación: Una de las propiedades más notables de la goma gellan de alto contenido en acilo es su capacidad para formar geles. A diferencia de muchos otros agentes gelificantes, puede producir una gran variedad de texturas, desde firmes y quebradizas hasta blandas y elásticas, dependiendo de su concentración y de la presencia de cationes divalentes como el calcio o el magnesio.
- Estabilidad térmica: Esta goma presenta una notable estabilidad térmica. Puede soportar procesos a altas temperaturas, como la pasteurización y la esterilización, sin perder su capacidad gelificante ni sufrir una degradación significativa.
- Solubilidad: Es soluble en agua caliente, pero forma geles al enfriarse y fraguar. Esta propiedad es especialmente útil en procesos en los que el control del tiempo de gelificación es crucial.
- Estabilidad del pH: La Goma Gellan de alto contenido en acilo es estable en una amplia gama de niveles de pH, lo que la hace adecuada para su uso en productos de acidez variable, desde productos lácteos de pH neutro hasta bebidas ácidas.
- Interacciones sinérgicas: Puede interactuar sinérgicamente con otras sustancias, como la goma xantana, para modificar aún más la textura y la estabilidad.
Beneficios en la alimentación y otras industrias
- Industria alimentaria: En la industria alimentaria, sus aplicaciones son diversas. En los productos lácteos, mejora la textura y la estabilidad. En bebidas, evita la sedimentación de partículas en suspensión. Su uso en confitería da lugar a texturas variadas, desde masticables suaves a geles duros.
- Productos farmacéuticos y cosméticos: Más allá de la alimentación, la Goma Gellan de alto contenido en acilo encuentra aplicaciones en productos farmacéuticos como estabilizante en suspensiones y emulsiones, y en cosmética por sus propiedades espesantes y estabilizantes.
- Dietas especiales: Al ser vegana y no contener gluten, es adecuada para una amplia gama de preferencias y restricciones dietéticas, lo que la convierte en una opción versátil para los fabricantes de alimentos que atienden a diversas necesidades de los consumidores.
Impacto medioambiental y sostenibilidad
Su producción, predominantemente mediante fermentación microbiana, se considera respetuosa con el medio ambiente y sostenible. El proceso requiere menos recursos y tiene una menor huella de carbono en comparación con los gelificantes tradicionales derivados de animales o algas marinas.
4,Aplicaciones en la industria alimentaria
Las propiedades únicas de la goma gellan de alto contenido en acilo la han convertido en un ingrediente popular en diversos productos alimentarios. Su capacidad para modificar la textura, mejorar la estabilidad e interactuar con otros ingredientes ha propiciado su adopción generalizada en la industria alimentaria.
Productos lácteos
- Yogures y postres: Se utiliza para crear una textura suave y cremosa en los yogures. Evita la sinéresis (separación del agua), garantizando una calidad constante durante toda su vida útil. En postres como flanes y cremas, proporciona una estructura de gel estable pero suave.
- Queso: En los productos de queso, la goma gellan de alta acidez ayuda a conseguir la textura y firmeza deseadas, especialmente en quesos cremosos y quesos untables.
Bebidas
- Zumos y bebidas vegetales: Estabiliza la pulpa y otras partículas en suspensión de los zumos, evitando que se asienten. En bebidas de origen vegetal, como la leche de almendras o de soja, mantiene la homogeneidad y mejora la sensación en boca.
- Bebidas funcionales: En bebidas energéticas y suplementos nutricionales, ayuda a suspender vitaminas y minerales, garantizando una distribución uniforme en toda la bebida.
Productos de confitería y panadería
- Caramelos de goma y gominolas: Se utiliza mucho en la producción de caramelos de goma y gelatinas, que proporcionan una textura masticable pero suave.
- Rellenos y glaseados de panadería: Se utiliza para estabilizar rellenos y glaseados de panadería, evitando que se escurran o empapen el producto horneado.
Alimentos procesados
- Salsas y aderezos: En salsas y aderezos, la goma gellan de alto contenido en acilo actúa como estabilizante y espesante, mejorando la textura y asegurando la consistencia.
- Alternativas a la carne: En el sector en rápido crecimiento de las alternativas a la carne de origen vegetal, ayuda a formar una textura similar a la de la carne, mejorando la experiencia sensorial global.
Innovación y tendencias futuras
La versatilidad de la goma gellan de alta acidez impulsa continuamente la innovación en la formulación de alimentos. Una tendencia emergente es su uso en la impresión 3D de alimentos, donde sus propiedades gelificantes precisas permiten la creación de estructuras alimentarias complejas. Además, su compatibilidad con las tendencias de etiquetado limpio (natural, no transgénico, vegano) hace que sea una opción favorecida en el desarrollo de productos alimenticios más saludables.
4,Comparación con otros hidrocoloides
En el ámbito de la ciencia alimentaria, los hidrocoloides son esenciales por su capacidad para modificar la textura y la estabilidad de los productos alimenticios. La goma gellan de alto contenido en acilo, aunque tiene propiedades únicas, comparte escenario con otros hidrocoloides, cada uno con sus características distintivas. Comprender las diferencias y similitudes entre estas sustancias es crucial para los tecnólogos y fabricantes de alimentos.
Agar-Agar
- Origen: El agar-agar es un hidrocoloide vegetal derivado de algas rojas.
- Textura: Forma geles firmes y quebradizos, muy diferentes de los geles blandos y elásticos de la goma gellan de alto contenido en acilo.
- Temperaturas de fusión y gelificación: El agar tiene un punto de fusión más alto, lo que puede suponer una limitación en algunas aplicaciones.
Carragenina
- Tipos: Existen varios tipos de carragenanos (kappa, iota, lambda), cada uno de los cuales crea texturas diferentes.
- Aplicaciones lácteas: En los productos lácteos, a menudo se prefiere la carragenina por su capacidad para interactuar con las proteínas de la leche, una propiedad menos pronunciada en la Goma Gellan con alto contenido en acilo.
Goma garrofín
- Sinergia con otras gomas: La goma garrofín suele requerir la combinación con otras gomas como la xantana para conseguir la textura deseada, mientras que la goma gellan de alto contenido en acilo puede funcionar eficazmente por sí sola.
Goma xantana
- Estabilidad: La goma xantana proporciona una excelente estabilidad en una amplia gama de temperaturas y niveles de pH, similar a la goma gellan de alto contenido en acilo.
- Viscosidad: La goma xantana aumenta principalmente la viscosidad de una solución, sin formar un verdadero gel.
Pectina
- A base de fruta: La pectina se obtiene de las frutas y se utiliza habitualmente en mermeladas y jaleas.
- Gelificación dependiente del azúcar y el ácido: La pectina necesita azúcar y ácido para formar geles, a diferencia de la goma gellan de alto acilo, que gelifica en presencia de iones.
Resumen comparativo
- Versatilidad: La goma gellan de alto contenido en acilo es más versátil en texturas de gel que el agar-agar y la pectina.
- Estabilidad térmica: Ofrece mejor estabilidad térmica que la mayoría de los demás hidrocoloides.
- Funcional en bajas cantidades: Es eficaz a concentraciones más bajas que la carragenina o la goma garrofín, lo que la convierte en una opción rentable.
Comprender estas diferencias permite a los científicos de la alimentación seleccionar el hidrocoloide más adecuado para aplicaciones específicas, teniendo en cuenta factores como la textura deseada, las condiciones de procesado y el coste.
6,Aspectos sanitarios y nutricionales de la goma gellan rica en acilo
La goma gellan de alto contenido en acilo no sólo se valora por sus propiedades funcionales en alimentos y otros productos, sino también por su compatibilidad con diversas consideraciones sanitarias y dietéticas. Entender su impacto en la salud y la nutrición es crucial, sobre todo teniendo en cuenta la creciente concienciación de los consumidores y la demanda de productos alimentarios que favorezcan estilos de vida saludables.
Seguridad y reglamentación
- Autorización de las autoridades: Está reconocido como seguro por las principales autoridades de seguridad alimentaria, incluida la FDA en Estados Unidos y la EFSA en Europa.
- Sin alérgenos: No contiene alérgenos comunes, por lo que es adecuado para personas con alergias o intolerancias.
Consideraciones dietéticas
- Veganos y vegetarianos: Como producto derivado de la fermentación, la Goma Gellan de alto contenido en acilo es apta para dietas veganas y vegetarianas.
- Sin gluten: No contiene gluten por naturaleza, lo que es importante para las personas celíacas o sensibles al gluten.
- Bajo en calorías: Aporta mínimas o ninguna caloría, beneficioso para las dietas de control de calorías.
Salud intestinal y digestibilidad
- Digestibilidad: Aunque no es digerible por el cuerpo humano, no se sabe que afecte negativamente a la salud intestinal.
- Potencial prebiótico: Algunos estudios sugieren posibles efectos prebióticos, aunque se necesita más investigación en este campo.
Impacto en el azúcar en sangre y el colesterol
- Niveles de azúcar en sangre: Al ser un hidrato de carbono no digerible, no influye en los niveles de azúcar en sangre, por lo que es apto para diabéticos.
- Colesterol: Los estudios preliminares indican que puede tener efectos reductores del colesterol, pero se necesitan investigaciones más exhaustivas para confirmar estos beneficios.
Uso en productos bajos en azúcar y grasa
- Modificación de texturas: Su capacidad para modificar la textura es especialmente valiosa en productos reducidos en azúcar y bajos en grasa, donde puede compensar cambios en la sensación en boca y la consistencia.
Aspectos éticos y medioambientales
- Sostenibilidad: El proceso de fermentación microbiana utilizado en su producción se considera sostenible y ético desde el punto de vista medioambiental, con una huella ecológica menor en comparación con los productos de origen animal.
En conclusión, la goma gellan de alto contenido en acilo no sólo es un hidrocoloide versátil y eficaz, sino que también se ajusta bien a las consideraciones actuales en materia de salud, nutrición y medio ambiente. Esta alineación con las tendencias dietéticas modernas y la sostenibilidad lo convierten en un ingrediente preferido en la formulación de diversos productos alimenticios.
7,Panorama normativo y de mercado de la goma gellan de alto contenido en acilo
El panorama normativo y la dinámica del mercado de la goma gellan de alto contenido en acilo proporcionan información sobre su aceptación global, tendencias de uso y potencial de crecimiento futuro. Esta panorámica examina su situación reglamentaria, su posicionamiento en el mercado y los factores que impulsan su demanda en diversos sectores.
Situación reglamentaria
- Aprobación mundial: Los principales organismos reguladores de todo el mundo, como la FDA (EE.UU.), la EFSA (Unión Europea) y la FSSAI (India), han aprobado el uso de la goma gellan de alto contenido en acilo en productos alimentarios y farmacéuticos.
- Requisitos de etiquetado: La normativa relativa al etiquetado varía según el país. En algunas regiones, debe figurar como aditivo con su respectivo número E (E418).
- Límites de uso: Los organismos reguladores suelen especificar los niveles máximos permitidos en diferentes categorías de alimentos, garantizando así la seguridad de los consumidores.
Dinámica del mercado
- Impulsores de la demanda: Los principales impulsores son su versatilidad como gelificante, su compatibilidad con diversas necesidades dietéticas (vegano, sin gluten) y su papel en la mejora de las cualidades sensoriales de los productos alimentarios.
- Aumentar la conciencia sanitaria: La creciente concienciación de los consumidores sobre la salud y el bienestar está impulsando la demanda de ingredientes naturales y de etiquetado limpio, lo que beneficia a la goma gellan de alto contenido en acilo.
- Innovación en tecnología alimentaria: Los avances en el procesado de alimentos y la demanda de nuevos productos alimentarios están impulsando aún más su uso.
Aplicaciones industriales
- Sector de alimentación y bebidas: Este sector sigue siendo el mayor consumidor, aprovechando sus propiedades texturales y su estabilidad.
- Productos farmacéuticos y nutracéuticos: Su uso en sistemas de administración de fármacos y como estabilizador en formulaciones está en expansión.
- Cosmética y cuidado personal: Un ámbito emergente, impulsado por su origen natural y sus propiedades estabilizadoras.
Tendencias del mercado mundial
- Previsiones de crecimiento: Los estudios de mercado indican una trayectoria de crecimiento constante, atribuida a la expansión de las aplicaciones y a las tendencias alimentarias mundiales.
- Variaciones regionales: La penetración en el mercado varía, con un mayor uso en regiones con industrias avanzadas de procesamiento de alimentos.
- Cadena de suministro y sostenibilidad: El abastecimiento y los métodos de producción sostenibles se están convirtiendo en factores cruciales que influyen en el crecimiento del mercado.
Perspectivas de futuro
El futuro del alto contenido en acilo Goma Gellan parece prometedor, impulsado por su adaptabilidad a diversas aplicaciones y su alineación con las tendencias mundiales hacia opciones alimentarias más sanas y sostenibles. Es probable que la continua innovación en ciencia y tecnología alimentarias abra nuevas vías para su aplicación, consolidando aún más su posición en el mercado.
En resumen, la combinación de versatilidad funcional, alineación sanitaria y aprobación reglamentaria de la goma gellan de alto contenido en acilo la posiciona como un ingrediente valioso en una amplia gama de industrias, con una perspectiva positiva de crecimiento e innovación continuos.
